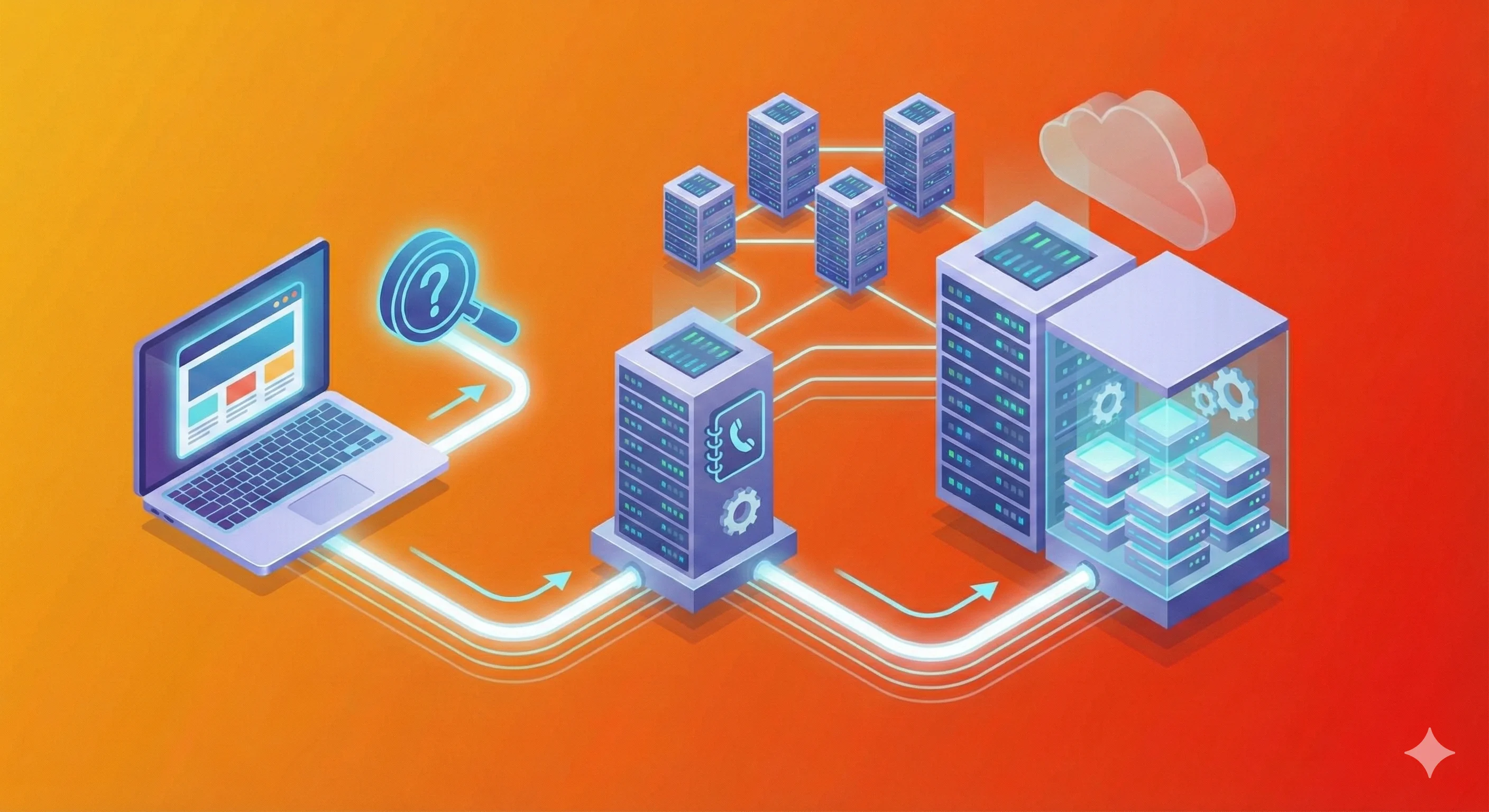
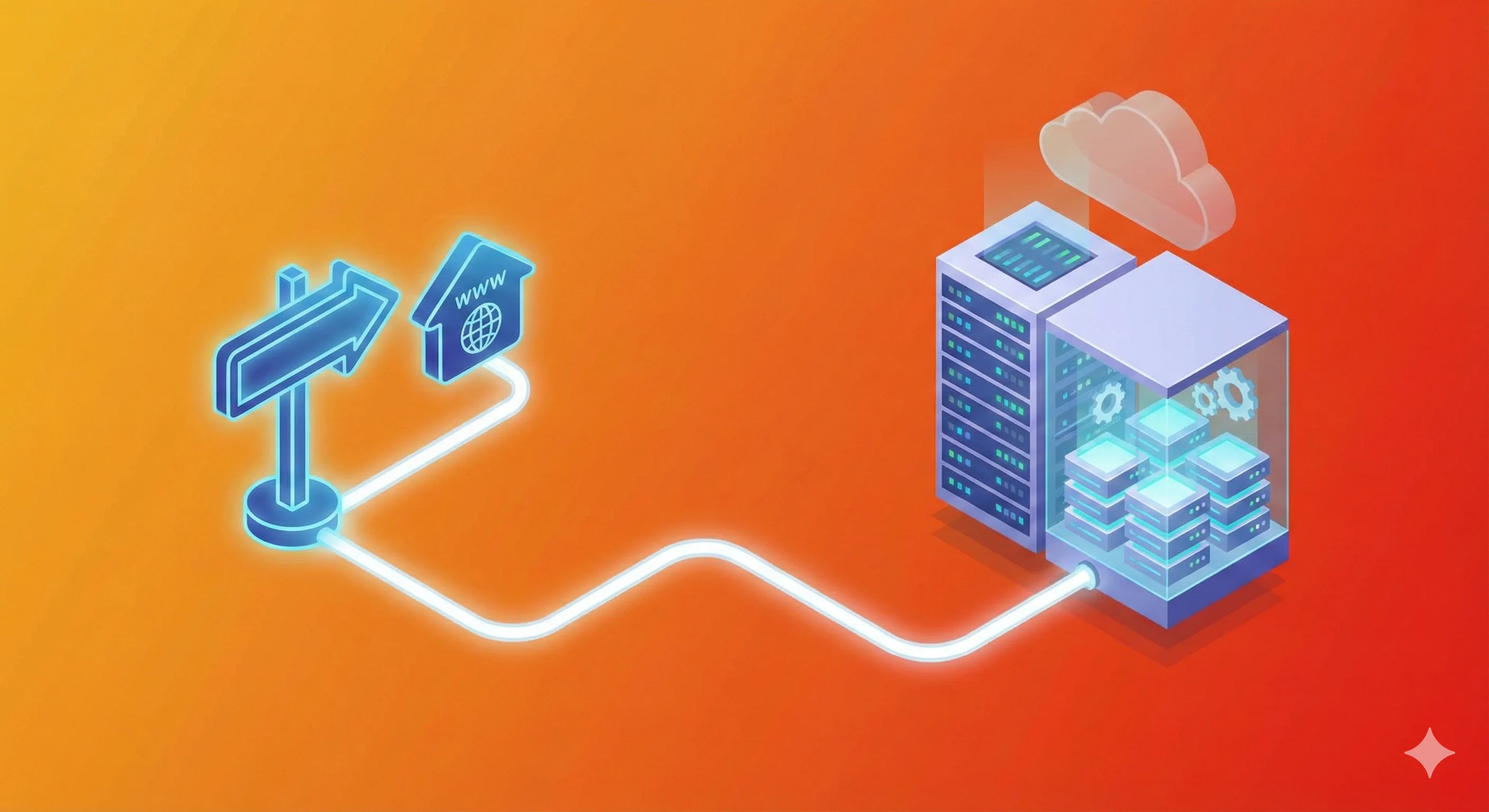
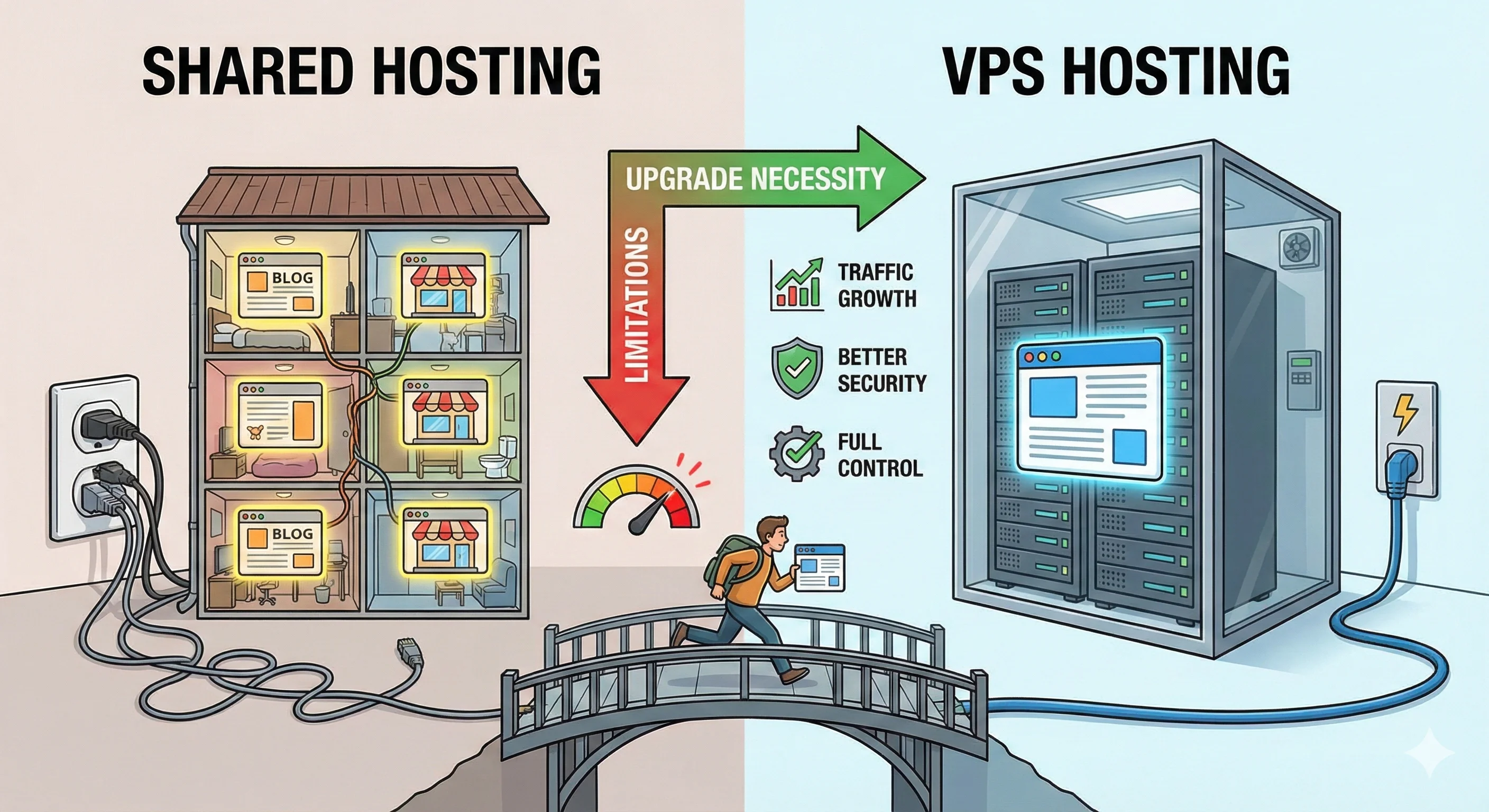
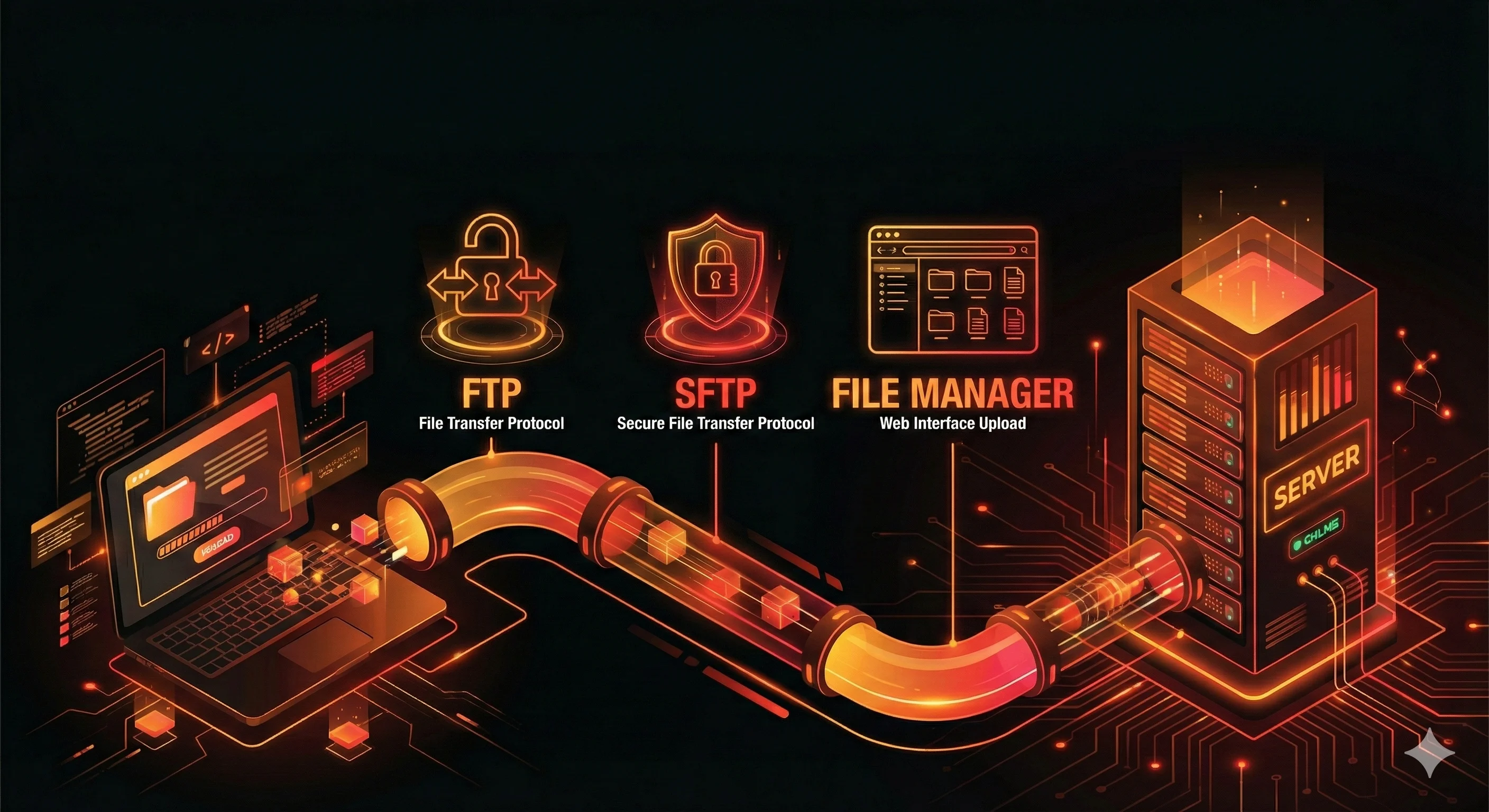
DNS is an essential background system that translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, allowing browsers to connect to the correct servers. It works like the internet’s address book, enabling websites, email, and many online services to function reliably. By using caching and a hierarchical lookup process, DNS also improves browsing speed and supports scalable infrastructure through traffic distribution across multiple servers.